| Director | Tokyo Healthcare University Graduate School Division of Infection Prevention and Control, Prof. Takashi Okubo |
|---|---|
| POINT | The closed method for easy cleaning operation is introduced here. The key is to perform the operation without touching the caregiver when operating the belt guide. Please tuck the top underwear hem into the pants. |
| Mekkin Gown Fitting Guide (in Japanese only) |
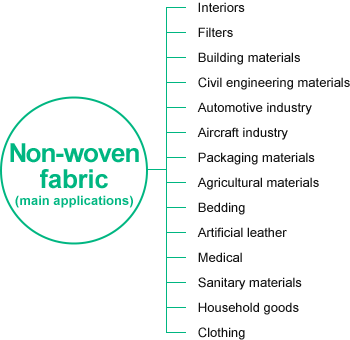
Basic Knowledge of Non-woven Fabric
Non-woven fabric is a material that lies between cloth and paper.
The performance of non-woven fabric is determined by:
1. Raw material
2. Manufacturing method
3. Processing
Via the combination of these three factors, characteristics such as thickness, softness, chemical resistance, air
permeability, abrasion resistance, elasticity, and flexibility are brought out, creating non-woven fabric according to
usage. Here, we would like to focus on medical non-woven fabric and to introduce the manufacturing methods.
Manufacturing Process for Medical-use Non-woven Fabric
It has been more than 30 years since non-woven fabric was used in infection control measures on the medical frontlines. Today, usage is expanding, and such fabric is used for all related occasions. The variations and manufacturing methods have been evolving accordingly.
| Name | Spunlace | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing method | A manufacturing method in which high-pressure water is sprayed into the web (cotton-like fibers) by nozzles and where the fibers are interlaced by water flow | ||
| Characteristics | Finely woven Cloth-like texture |
Main applications | Surgical drapes Surgical gowns |
| Name | Meltblown | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing method | A manufacturing method that collects the melted material that has been blown off with high-temperature air when pushed out from the nozzle to form a web | ||
| Characteristics | Finely woven Low strength |
Main applications | Surgical drapes and filters Surgical gowns |
| Name | Spunbond Meltblown Spunbond (SMS) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing method | A manufacturing method that combines spunbond (high strength) and meltblown (high barrier properties) into a single sheet | ||
| Characteristics | According to the characteristics of spunbond and meltblown | Main applications | Surgical drapes and sterilization wraps (kurumu) Surgical gowns |
| Name | Flashspun | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing method | "Flashspun" refers to the rapid gasification of liquid. The spunbond process uses this gasification phenomenon to produce ultra-fine, web-like continuous fibers. | ||
| Characteristics | Lightweight High strength Less dust generation |
Main applications | Surgical drapes Surgical gowns |
Testing Methods for Medical-use Non-woven Fabric
There are common tests for medical use non-woven fabric, and the materials are selected under a strict examination process. The most-important thing in this process is the balance of evaluation. Since the desired texture and safety differ depending on the intended use of the final product, it is not necessary that all evaluations show the highest value.
| Test items | Test standard | Test method | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | JIS L 1912 | Prepare a test piece, fix it to the testing equipment, and measure the maximum strength when it is pulled and cut at a constant speed. | The higher the value, the less the possibility of rupture. |
| Tear strength | JIS L 1912 | Prepare a test piece (short side), and then cut a slit in the center. Pinch both ends of the slit, and then measure the maximum load when it is pulled at a constant speed. | The higher the value, the less the possibility of rupture. |
| Water repellency | JIS L 1912 | Fix the test piece on an inclined stand and spray 250 ml of water from a height of 15 cm. Observe the surface condition of the test piece after spraying and visually assess it on a scale of 1 to 5. | The higher the value (score), the higher the water repellency. |
| Alcohol repellency | JIS L 1912 | Pour an alcohol solution onto the test piece and leave it for 5 minutes, and then observe from the back side to see the penetration of the solution. Repeat the measurement with different concentrations of the solution and use the maximum concentration that does not penetrate as the alcohol repellency score. | The higher the value (score), the higher the alcohol repellency. |
| Water pressure resistance | JIS L 1912 | Apply water pressure to the test piece using special test equipment, and then measure the water level when water comes out from three points on the test piece. | The higher the value, the higher the barrier against water. |
| Flexibility | JIS L 1912 | The test piece is slid on an inclined measuring device, and the distance traveled when the tip reaches the inclination is measured. | The lower the value, the higher the flexibility. |
| Permeability | JIS L 1912 | Apply a certain pressure on the test piece, and then calculate the amount of air that passes through the test piece. | The higher the value, the higher the air permeability. |
What is required for medical-use non-woven fabric?
HOGY Medical believes that the following points are essential for the performance of non-woven fabrics on the medical frontlines in order to find the best combination of raw materials and manufacturing methods from the viewpoint of nosocomial infection control.
Materials that serve as a barrier for bacteria
(1) Water repellency or waterproof capability
(2) High-density mesh
(3) Permeability
(4) Tensile and tear strength
(5) Stitch strength
(6) Flexibility
(7) Lightweight
(8) Lint-free
(9) Non-hazardous
(10) Easy disposal
Materials for water absorbency
(1) Fast water absorption
(2) Large amount of water absorption
(3) Non-hazardous
(4) Flexibility
(5) Lint-free
(6) High wet strength
(7) Easy disposal
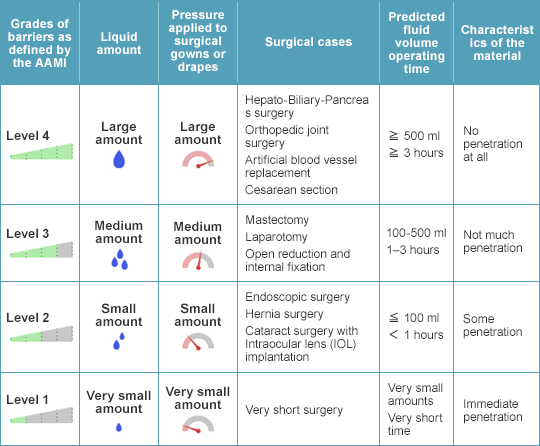
Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) is a U.S. organization that aims to increase understanding of proper use of medical instruments. It has established standards for proper use of medical instruments (standards for safety and performance). One of these standards is the standard for four-step barrier performance for surgical drapes, gowns, and other protective clothing. In recent years, products have been evaluated based on these standards, and the standards are now functioning as a set of unified standards for the industry.
HOGY Medical's Non-woven Fabrics for Medical Use
HOGY Medical uses materials that meet various requirements for medical use and responds to customer requests by manufacturing a wide variety of products. As for surgical drapes, our approach is to customize the position and size of the incise area and the overall size of the surgical drape according to evolving surgical techniques and customer usage, and to proceed with product manufacturing in consultation with our customers.
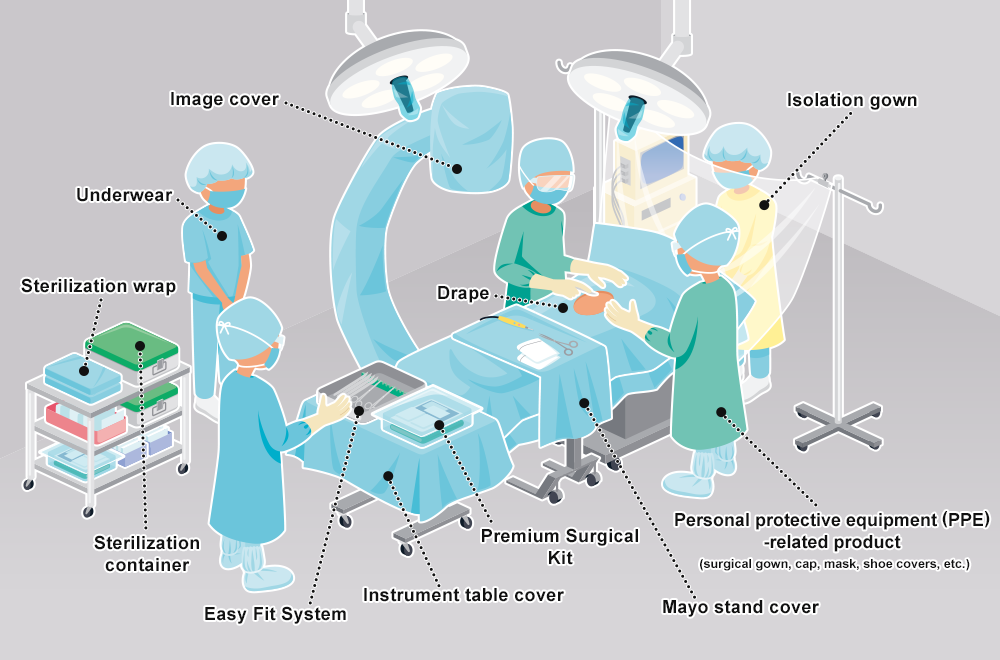
| Wearables | Surgical gowns, caps, masks, aprons, underwear, isolation gowns, patient gowns, staff jumpers, workwear |
|---|---|
| Surgical drape covers, etc. | Surgical drapes, mayo stand covers, arm covers, sheets, image covers, instrument table covers, leggings covers |
| Other | Sterilization wraps/towels |
Wearing Guide
In order to maximize the safety features of non-woven fabric, please refer to the following recommended procedures so as to use the products correctly.
Gown Wearing Guide
Cap and Mask Fitting Guide
| Director | Tokyo Healthcare University graduate School Division of Infection Prevention and Control, Prof. Takashi Okubo |
|---|---|
| POINT | Cap: It should be worn to cover the hair as much as possible. In the case of surgery where the doctor's or nurse's head
is positioned directly over the surgical area, wear a type that can completely cover the hair. Mask: The key is to fit it to the face so that the exhaled and inhaled air passes through the filter as much as possible. |
| Cap and Mask Fitting Guide (in Japanese only) |
Surgical Glove Fitting Guide
| Director | Tokyo Healthcare University Graduate School Division of Infection Prevention and Control, Prof. Takashi Okubo |
|---|---|
| POINT | The closed method for one person to perform easy cleaning operation is introduced here. |
| Surgical Glove Fitting Guide (in Japanese only) |
Precaution Set Dressing and Undressing Guide
| Director | HOGY MEDICAL CO., LTD. |
|---|---|
| POINT | Introduces how to put it on safely |
| Precaution Set Dressing and Undressing Guide (in Japanese only) |